Page 22 - Steel Tech India eMagazine Volume January 2023
P. 22
92/ Ć ,668( Ć 2FWREHU
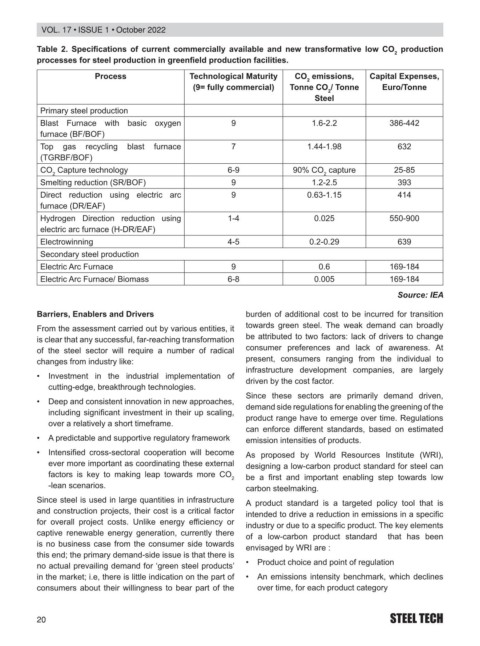
7DEOH 6SHFL¿FDWLRQV RI FXUUHQW FRPPHUFLDOO\ DYDLODEOH DQG QHZ WUDQVIRUPDWLYH ORZ &2 production
2
SURFHVVHV IRU VWHHO SURGXFWLRQ LQ JUHHQ¿HOG SURGXFWLRQ IDFLOLWLHV
Process Technological Maturity CO emissions, Capital Expenses,
2
(9= fully commercial) Tonne CO / Tonne Euro/Tonne
2
Steel
Primary steel production
Blast Furnace with basic oxygen 9 1.6-2.2 386-442
IXUQDFH %) %2)
Top gas recycling blast furnace 7 1.44-1.98 632
7*5%) %2)
CO Capture technology 6-9 90% CO capture 25-85
2 2
6PHOWLQJ UHGXFWLRQ 65 %2) 9 1.2-2.5 393
Direct reduction using electric arc 9 0.63-1.15 414
IXUQDFH '5 ($)
Hydrogen Direction reduction using 1-4 0.025 550-900
HOHFWULF DUF IXUQDFH + '5 ($)
Electrowinning 4-5 0.2-0.29 639
Secondary steel production
Electric Arc Furnace 9 0.6 169-184
(OHFWULF $UF )XUQDFH %LRPDVV 6-8 0.005 169-184
Source: IEA
Barriers, Enablers and Drivers burden of additional cost to be incurred for transition
From the assessment carried out by various entities, it towards green steel. The weak demand can broadly
is clear that any successful, far-reaching transformation be attributed to two factors: lack of drivers to change
of the steel sector will require a number of radical consumer preferences and lack of awareness. At
changes from industry like: present, consumers ranging from the individual to
infrastructure development companies, are largely
,QYHVWPHQW LQ WKH LQGXVWULDO LPSOHPHQWDWLRQ RI driven by the cost factor.
cutting-edge, breakthrough technologies.
Since these sectors are primarily demand driven,
'HHS DQG FRQVLVWHQW LQQRYDWLRQ LQ QHZ DSSURDFKHV demand side regulations for enabling the greening of the
LQFOXGLQJ VLJQL¿FDQW LQYHVWPHQW LQ WKHLU XS VFDOLQJ product range have to emerge over time. Regulations
over a relatively a short timeframe.
FDQ HQIRUFH GLႇHUHQW VWDQGDUGV EDVHG RQ HVWLPDWHG
$ SUHGLFWDEOH DQG VXSSRUWLYH UHJXODWRU\ IUDPHZRUN emission intensities of products.
,QWHQVL¿HG FURVV VHFWRUDO FRRSHUDWLRQ ZLOO EHFRPH As proposed by World Resources Institute (WRI),
ever more important as coordinating these external designing a low-carbon product standard for steel can
factors is key to making leap towards more CO
2 EH D ¿UVW DQG LPSRUWDQW HQDEOLQJ VWHS WRZDUGV ORZ
-lean scenarios. carbon steelmaking.
Since steel is used in large quantities in infrastructure A product standard is a targeted policy tool that is
and construction projects, their cost is a critical factor LQWHQGHG WR GULYH D UHGXFWLRQ LQ HPLVVLRQV LQ D VSHFL¿F
IRU RYHUDOO SURMHFW FRVWV 8QOLNH HQHUJ\ HႈFLHQF\ RU LQGXVWU\ RU GXH WR D VSHFL¿F SURGXFW 7KH NH\ HOHPHQWV
captive renewable energy generation, currently there of a low-carbon product standard that has been
is no business case from the consumer side towards envisaged by WRI are :
this end; the primary demand-side issue is that there is
no actual prevailing demand for ‘green steel products’ 3URGXFW FKRLFH DQG SRLQW RI UHJXODWLRQ
in the market; i.e, there is little indication on the part of $Q HPLVVLRQV LQWHQVLW\ EHQFKPDUN ZKLFK GHFOLQHV
consumers about their willingness to bear part of the over time, for each product category
STEEL TECH