Page 12 - Steel Tech India eMagazine Volume January 2023
P. 12
92/ Ć ,668( Ć 2FWREHU
C2, and C3 the data can be discretely quantitative The measurement of consistency in AHP is Consistency
measured in terms of numbers and criteria C4 and C5 Ratio (CR). For determining the CR, we shall use two
are qualitative or subjective, e.g., the data may say that more ratios, called Consistency Index (CI) and Random
V1 is not so reputed with not-so-strong track record Index (RI). Since the mathematical derivation of AHP
(criteria C4) compared to V3 or that V3 is better than process or its components is beyond the scope of this
V2 in criteria C5 etc. AHP converts all these judgmental article, the method of working shall only be explained
data into quantitative measures and then treat the when we illustrate the methodology of analytics for
problem mathematically to reach the right decision on arriving at the right decision on selection of appropriate
site selection. vendor.
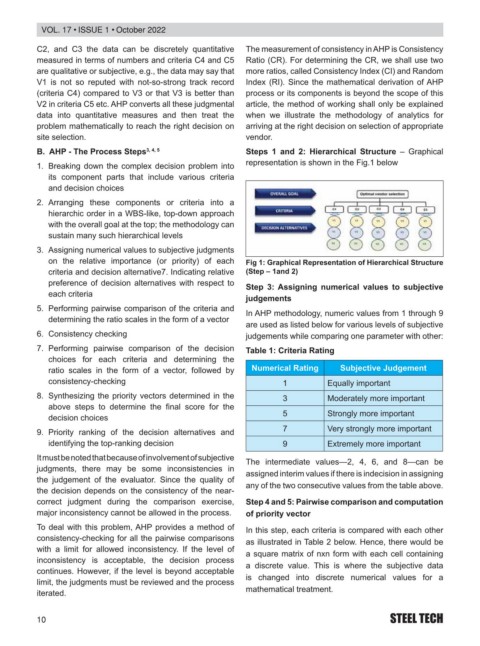
B. AHP - The Process Steps 3, 4, 5 Steps 1 and 2: Hierarchical Structure – Graphical
representation is shown in the Fig.1 below
1. Breaking down the complex decision problem into
its component parts that include various criteria
and decision choices
2. Arranging these components or criteria into a
hierarchic order in a WBS-like, top-down approach
with the overall goal at the top; the methodology can
sustain many such hierarchical levels
3. Assigning numerical values to subjective judgments
on the relative importance (or priority) of each Fig 1: Graphical Representation of Hierarchical Structure
criteria and decision alternative7. Indicating relative (Step – 1and 2)
preference of decision alternatives with respect to Step 3: Assigning numerical values to subjective
each criteria
judgements
5. Performing pairwise comparison of the criteria and In AHP methodology, numeric values from 1 through 9
determining the ratio scales in the form of a vector
are used as listed below for various levels of subjective
6. Consistency checking judgements while comparing one parameter with other:
7. Performing pairwise comparison of the decision Table 1: Criteria Rating
choices for each criteria and determining the
ratio scales in the form of a vector, followed by Numerical Rating Subjective Judgement
consistency-checking 1 Equally important
8. Synthesizing the priority vectors determined in the 3 Moderately more important
DERYH VWHSV WR GHWHUPLQH WKH ¿QDO VFRUH IRU WKH
decision choices 5 Strongly more important
9. Priority ranking of the decision alternatives and 7 Very strongly more important
identifying the top-ranking decision 9 Extremely more important
It must be noted that because of involvement of subjective The intermediate values—2, 4, 6, and 8—can be
judgments, there may be some inconsistencies in assigned interim values if there is indecision in assigning
the judgement of the evaluator. Since the quality of
the decision depends on the consistency of the near- any of the two consecutive values from the table above.
correct judgment during the comparison exercise, Step 4 and 5: Pairwise comparison and computation
major inconsistency cannot be allowed in the process. of priority vector
To deal with this problem, AHP provides a method of In this step, each criteria is compared with each other
consistency-checking for all the pairwise comparisons as illustrated in Table 2 below. Hence, there would be
with a limit for allowed inconsistency. If the level of a square matrix of nxn form with each cell containing
inconsistency is acceptable, the decision process a discrete value. This is where the subjective data
continues. However, if the level is beyond acceptable
limit, the judgments must be reviewed and the process is changed into discrete numerical values for a
iterated. mathematical treatment.
STEEL TECH